Starting a business is an exciting journey with highs and lows.
For early-stage startups and founders, creating a product that customers will love is not just a goal—it’s the key to survival and success in a competitive landscape.
Enter design thinking—a mindset and approach to problem-solving and innovation anchored around human-centered design. Design thinking is used by some of the world’s leading brands, such as Apple, Google, and Samsung, to help them create more customer-focused products and services.
What is design thinking and how will it help you create a product that customers will love? Let’s explore:
What is design thinking?
Design thinking is an iterative process in which you seek to understand your customers or users, challenge assumptions, define problems, and create innovative solutions to problems.
It differs from other innovation and ideation processes in that it’s solution-based and user-centric rather than problem-based. This means it helps you make products or services that people love because it puts the focus on what users need and involves trying and refining ideas until you get it right.
Design thinking is incredibly important and useful for startups at all stages of development, whether you’re in the early stages or have a successful product and business model.
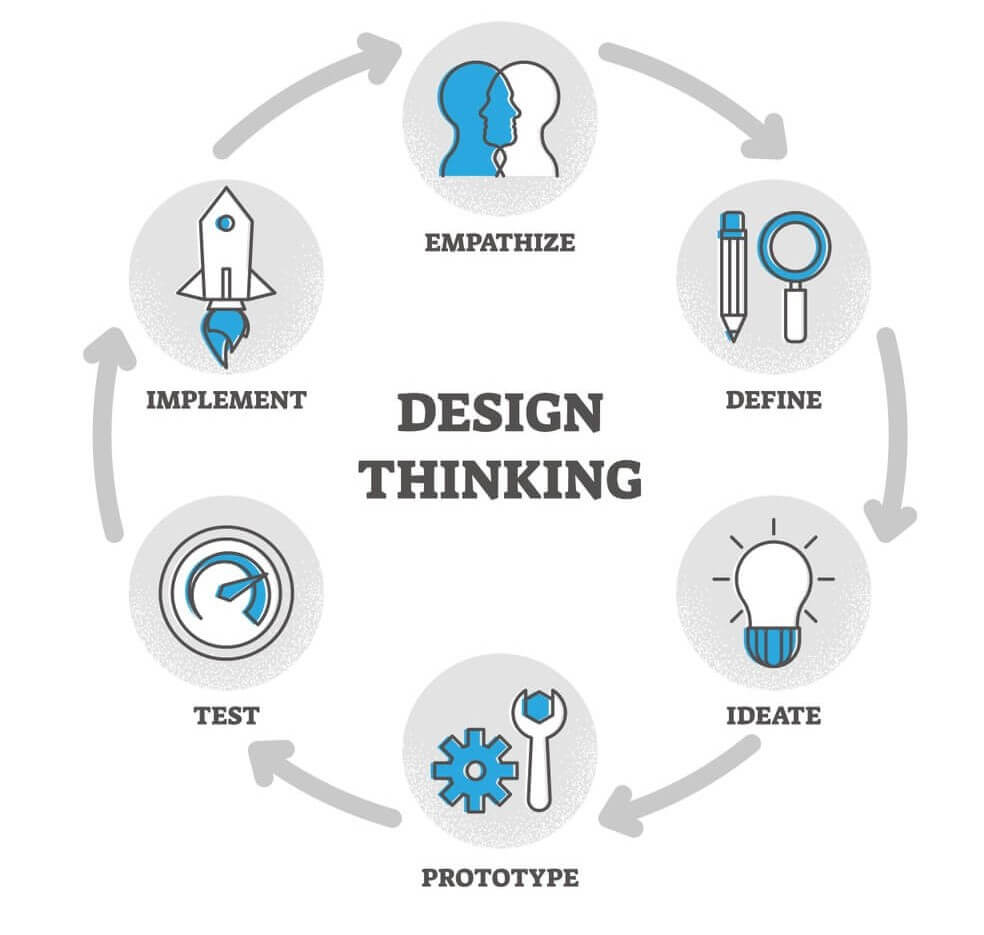
What is the design thinking process?
The design thinking process involves five distinct stages: empathise, define, ideate, prototype, and test. Each stage can be carried out in parallel, repeated, and circled back to the previous stage at any point in the process.
Let’s dive into each stage of the design thinking process and how it will help create products that customers will love:
Empathize:
Understanding the needs and perspectives of your target audience, including their challenges and desires.
In the Empathize stage, the key goal is to deeply understand your users, their needs, and the problems that will underlie the development of the product you want to create. Conduct interviews, surveys, or observations to gain insights into their problems and preferences. This will help you tailor your products or services to meet real user needs.
Define:
Clearly articulate the problem based on the insights gathered during the empathize stage. Define the challenge you aim to address.
Based on your understanding of the users in step one, define the problem that you intend to solve. What are the users experiencing? What is the problem? You should identify their needs and any insights gained from the first stage. A problem statement should look something like this:
(User persona) wants a solution for (user’s need) because of (insights).
Ideate
Generate a wide range of creative and innovative ideas without judgement.
In the third stage of design thinking, it’s time to brainstorm ideas. You’ve grown to understand your users and their needs in the Empathize stage, and you’ve analysed your observations in the Define stage to create a user-centric problem statement. With this foundation, you can explore various solutions to your problem statement.
There are many ideation techniques you can use to ideate, which include brainstorming and mind mapping.
Prototype
Build tangible representations of your ideas to quickly and cheaply test and iterate.
After brainstorming ideas, pick the best ones and create prototypes—working models that you can use, apply, and showcase to people. Prototyping helps validate assumptions and gather valuable feedback to refine your offering.
By the end of the prototype stage, you’ll have a better idea of the product’s limitations and the problems it faces. You’ll also have a clearer view of how real users would behave, think, and feel when they interact with the end product.
Test
Implement your prototypes and gather feedback from users. Use this feedback to refine and improve your solutions.
Actively involve your target audience in the testing phase. From testing and gathering their feedback, you’ll understand what they like, what does not work, and any questions they have.
It is important to note that the five stages of design thinking are not always sequential. They do not have to follow a specific order, and they can often occur in parallel or be repeated iteratively. The stages should be understood as different modes that contribute to the entire process, rather than sequential steps.
Why does design thinking matter?
Design thinking is essentially a problem-solving approach that has the intention of improving products.
From innovation, creativity, and creating a user-centric business to effective problem solving, learning the design thinking process is valuable for several reasons:

- User-Centric Solutions: Learning this process ensures that solutions are tailored to meet real user needs, increasing the likelihood of success in the market.
- Innovation and Creativity: Importance: It encourages a creative and iterative approach to problem-solving—to think outside the box, fostering innovation in the development of products, services, or solutions.
- Effective Problem-Solving: It provides a systematic method for approaching and solving complex problems, equipping you with tools to define problems, ideate solutions, and test and refine them efficiently.
- Adaptability and Flexibility: It is adaptable and can be applied across various industries and contexts. Learning this process equips individuals with a versatile problem-solving framework that can be tailored to different challenges.
- User Feedback Integration: It helps in incorporating user insights early in the development cycle, reducing the risk of creating solutions that do not meet user expectations.
- Customer-Centric Business: Learning design thinking facilitates the creation of products and services that resonate with customers, contributing to long-term success.
Learning design thinking
For entrepreneurs and startups, design thinking is particularly valuable. It provides a structured approach to problem-solving in dynamic and uncertain environments, helping in the development of innovative and user-friendly products or services.
Are you ready to develop your design-thinking skills? Explore our online courses to discover how to leverage fundamental design thinking principles and innovative problem-solving tools in your startup. Click here to get started today: https://leet-academy.teachable.com/courses/




